Portal:History
The History Portal
History (derived from Ancient Greek ἱστορία (historía) 'inquiry; knowledge acquired by investigation') is the systematic study and documentation of the human past. History is an academic discipline which uses a narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians debate the nature of history as an end in itself, and its usefulness in giving perspective on the problems of the present.
The period of events before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts or traditional oral histories, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers.
Stories common to a particular culture, but not supported by external sources (such as the tales surrounding King Arthur), are usually classified as cultural heritage or legends. History differs from myth in that it is supported by verifiable evidence. However, ancient cultural influences have helped create variant interpretations of the nature of history, which have evolved over the centuries and continue to change today. The modern study of history is wide-ranging, and includes the study of specific regions and certain topical or thematic elements of historical investigation. History is taught as a part of primary and secondary education, and the academic study of history is a major discipline in universities.
Herodotus, a 5th-century BCE Greek historian, is often considered the "father of history", as one of the first historians in the Western tradition, though he has been criticized as the "father of lies". Along with his contemporary Thucydides, he helped form the foundations for the modern study of past events and societies. Their works continue to be read today, and the gap between the culture-focused Herodotus and the military-focused Thucydides remains a point of contention or approach in modern historical writing. In East Asia a state chronicle, the Spring and Autumn Annals, was reputed to date from as early as 722 BCE, though only 2nd-century BCE texts have survived. The title "father of history" has also been attributed, in their respective societies, to Sima Qian, Ibn Khaldun, and Kenneth Dike. (Full article...)
Featured picture
Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that fifteen future Pro Football Hall of Fame players have been drafted by the Detroit Lions?
- ... that former child refugee Ann Beaglehole has become a historian specialising in refugee history?
- ... that the market hall of Niort opened in 1871 and has been listed as a historic monument since 1987?
- ... that archaeologist Lawrence H. Keeley refined the methods of microscopic use-wear analysis to learn about prehistoric stone tools?
- ... that Dean Faithfull was the oldest player in NCAA Division II football history?
- ... that Chunyu Yi may have been the "ancient founder of the case history tradition"?
George Wilcken Romney (July 8, 1907 – July 26, 1995) was an American businessman and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served as chairman and president of American Motors Corporation from 1954 to 1962, the 43rd governor of Michigan from 1963 to 1969, and 3rd secretary of Housing and Urban Development from 1969 to 1973. He was the father of Mitt Romney, who serves as one of the United States senators from Utah and formerly was a governor of Massachusetts and the 2012 Republican presidential nominee; the husband of 1970 U.S. Senate candidate Lenore Romney; and the paternal grandfather of former Republican National Committee chair Ronna McDaniel.
Romney was born to American parents living in the Mormon colonies in Mexico; events during the Mexican Revolution forced his family to flee back to the United States when he was a child. The family lived in several states and ended up in Salt Lake City, Utah, where they struggled during the Great Depression. Romney worked in a number of jobs, served as a Mormon missionary in the United Kingdom, and attended several colleges in the U.S. but did not graduate from any of them. In 1939, he moved to Detroit and joined the American Automobile Manufacturers Association, where he served as the chief spokesman for the automobile industry during World War II and headed a cooperative arrangement in which companies could share production improvements. He joined Nash-Kelvinator Corporation in 1948, and became the chief executive of its successor, American Motors, in 1954. There he turned around the struggling firm by focusing all efforts on the compact Rambler car. Romney mocked the products of the "Big Three" automakers as "gas-guzzling dinosaurs" and became one of the first high-profile, media-savvy business executives. Devoutly religious, he presided over the Detroit stake of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. (Full article...)
On this day
November 11: Armistice Day (known as Remembrance Day in the Commonwealth of Nations and Veterans Day in the United States); Singles' Day in China and Southeast Asia
- 1778 – American Revolutionary War: British forces and their Iroquois allies attacked a fort and the village of Cherry Valley, New York, killing 14 soldiers and 30 civilians.
- 1813 – War of 1812: British–Canadian forces repelled an American attack at the Battle of Crysler's Farm, forcing the United States to give up their attempt to capture Montreal.
- 1934 – The Shrine of Remembrance (pictured), a memorial to all Australians who have served in war, opened in Melbourne.
- 1999 – The House of Lords Act was given royal assent, removing most hereditary peers from the British House of Lords.
- 2008 – After 30 years in power, Maumoon Abdul Gayoom was succeeded by Mohamed Nasheed as president of the Maldives.
- Martha Annie Whiteley (b. 1866)
- Édouard Vuillard (b. 1868)
- Maria Teresa de Filippis (b. 1926)
- Leonardo DiCaprio (b. 1974)
Selected quote
I hate this fast growing tendency to chain men to machines in big factories and deprive them of all joy in their efforts — the plan will lead to cheap men and cheap products.
— Richard Wagner, 19th century German composer
Related portals
More Did you know...
- ... that the anti-religious campaign culminating in the Stalinist show trial of the Kraków Curia (pictured) led to the imprisonment of 123 Polish Roman Catholic priests in just one year?
- ... that Confederate brigadier general Alfred E. Jackson was pardoned by President Andrew Johnson because of his kindness toward Johnson's family during the Civil War?
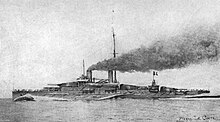
- ... that after HMS Porcupine was nearly split in two by a torpedo, the halves were nicknamed HMS Pork and HMS Pine?
- ... that the Experiment was a boat powered by horses running on a treadmill and propelled by a then-novel type of screw propeller?
- ... that one of the highest-ranking generals in China was injured in battle nine times?
- ... that in Mesopotamian mythology, the Apkallu were sent by the god Enki, from Dilmun to teach human beings various aspects of civilization?
- ... that Karl Marx's theory of historical trajectory attempted to prove the long-term unsustainability of capitalism?
- ... that in November 1921, the schooner Cymric collided with a tram in Dublin?
Topics
Categories

History • By period • By region • By topic • By ethnic group • Historiography • Archaeology • Books • Maps • Images • Magazines • Organizations • Fictional • Museums • Pseudohistory • Stubs • Timelines • Chronology • People • Wikipedia historians
WikiProjects
![]() WikiProject History •
Ancient Near East • Australian History • Classical Greece and Rome • Dacia • Former countries • History of Canada • Chinese history • European history • Heraldry and vexillology • Indian history • Jewish history • Medieval Scotland • Mesoamerica • Military history • Middle Ages • History of Science
WikiProject History •
Ancient Near East • Australian History • Classical Greece and Rome • Dacia • Former countries • History of Canada • Chinese history • European history • Heraldry and vexillology • Indian history • Jewish history • Medieval Scotland • Mesoamerica • Military history • Middle Ages • History of Science
WikiProject Time • Days of the Year • Years
WikiProject Biography • Composers • Political figures • Saints • United States Presidents
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus